بخشی از پاورپوینت
اسلاید 1 :
- پیچیدگی چندجمله ای
- پیچیدگی نمایی و فاکتوریل
Qاین الگوریتم ها برای مسائل با اندازه کوچک بد نیستند ولی با افزایش اندازه ورودی به شدت کند می شوند
اسلاید 2 :
- مساله کنترل ناپذیر
Qبرای مساله راه حلی با زمان چندجمله ای وجود ندارد
- مسائل رام نشدنی(Intractable)
Qاثبات می گردد که یافتن راه حل کارآمد غیر ممکن است مثلا یافتن کلیه مسیر های همیلتونی
- مسائل NP-Complete
Qمسائلی هستند که یافتن راه حل کارآمد برای آنها غیر ممکن نیست (ثابت نشده است رام نشدنی هستند) مانند کوله پشتی 0-1 و فروشنده دوره گرد و رنگ آمیزی گراف ها
Q
Q
اسلاید 3 :.
- الگوریتم قطعی:
Qنتیجه هر عمل کاملا معین و قطعی است مانند الگوریتم جستجوی دودویی و مرتب سازی و ...
Qکامپیوتر های قطعی
- الگوریتم غیر قطعی:
Qالگوریتمی است که دارای دستورات غیر قطعی است
Qدستورات غیر قطعی: دستوراتی که نتیجه اجرای آن از قبل قابل پیش بینی نیست(مثلا دستوری که از 100 عنصر یکی را انتخاب کند) یا دستورات مبتنی بر اعداد تصادفی
اسلاید 4 :
- تست تورینگ
Qtest defined by the mathematician Allen Turing for testing the ability of a machine to simulate human intelligence
- ماشين تورينگ (turing machine)
Qماشینی تئوری است که با دریافت ورودی ها اثبات ریاضی(حل مسائل) را انجام می دهد
Q
Q
Q
Q
Q
Qname for a theoretical machine that can make simple input/output actions which are used to in mathematical proofs
اسلاید 5 :
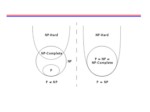
- Class of Problems
QP (Polynomial)
QNP (none-deterministic Polynomial)
fNP is the set of decision problems solvable in polynomial time by a non-deterministic Turing machine.
fNP is the class of decision problems for which there is a polynomially bounded non-deterministic algorithm
QNP-Complete
fA problem p in NP is also in NPC if and only if every other problem in NP can be transformed into p in polynomial time
QNP-Hard
fA problem H is NP-hard if and only if there is an NP-complete problem L that is polynomial time Turing-reducible to H
- Solving hard problems
QApproximation Algorithms
اسلاید 6 :
- چند جمله ایP (Polynomial) : مسائل تصمیم گیری که در زمان چند جمله ای توسط الگوریتم قطعی(ماشین تورینگ قطعی) قابل حل می باشد
- چند جمله ای غیر قطعی NP(none-deterministic Polynomial): مسائل تصمیم گیری که برای آن ها کسی راه حل چندجمله ای نیافته است اما توسط الگوریتم غیر قطعی(ماشین تورینگ غیر قطعی) در زمان چند جمله ای قابل حل است P Í NP
- NP-Complete: مساله P، NP-Complete است اگر NP باشد و سایر مسائل NP را در زمان چند جمله ای بتوان به آن تبدیل کرد
- NP-Hard: مساله H، NP-Hard است اگر وفقط اگر یک مساله NP-Compelete ، L وجود داشته باشد که در زمان چند جمله ای قابل تبدیل به H باشد
اسلاید 7 :
- تمام مسائلی که کنترل ناپذیری آنها ثابت شده است جزء مسایل NP نیستند
اسلاید 8 :
Qa formal notion of what a “problem” is
Qhigh-level description of a problem
- We define an abstract problem Q to be
Qa binary relation on
Qa set I of problem instances, and
Qa set S of problem solutions.
QQ ÎI ´ S
- Three Kinds of Problems
QDecision Problem
fe.g. Is there a solution better than some given bound?
QOptimal Value
fe.g. What is the value of a best possible solution?
QOptimal Solution
fe.g. Find a solution that achieves the optimal value.
اسلاید 9 :
Q// Data Structure
Qdescribing abstract problems (for solving by computers)
Qin terms of data structure or binary strings
- An encoding of a set S of abstract objects is
Qa mapping e from S to the set of binary strings.
- Encoding for Decision problems
QProblem instances, e : I à {0, 1}*
QSolution, e : S à {0, 1}
- “Standard” encoding
Qcomputing time may be a function of encoding
f// The size of the input (the number of bit to represent one input)
Qpolynomially related encodings
Qassume encoding in a reasonable concise fashion
اسلاید 10 :
Qproblem instances and solutions are represented in data structure or binary strings
Q// Language (in formal-language framework)
- We call a problem whose instance set (and solution set) is the set of binary strings a concrete problem.
- Computer algorithm solves concrete problems!
Qsolves a concrete problem in time O(T(n))
Qif provided a problem instance i of length n = |i|,
Qthe algorithm can produce the solution
Qin a most O(T(n)) time.
- A concrete problem is polynomial-time solvable
Qif there exists an algorithm to solve it in time O(nk)
Qfor some constant k. (also called polynomially bounded)