بخشی از پاورپوینت
--- پاورپوینت شامل تصاویر میباشد ----
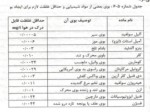
اسلاید 1 :
- وزن مولکولی
- حالت فیزیکی: جامد , مایع و گاز
- شکل فیزیکی
- رنگ
- بو
- اسیدیته
- حلالیت آب
- حلالیت در حلالهای آبی
- وزن مخصوص نسبت به آب (دانسیته )
- فرمول شیمیایی
- دمای انفجار
- دمای خود آتشگیری
- نقطه اشتعال
- نقطه ذوب
- نقطه جوش
- فشار بخار
اسلاید 2 :
- نقطه ذوب:
- دمایی است كه در آن دما یك جسم شروع به ذوب شدن می كند.
- نقطه جوش:
- دمایی است كه در آن دما یك جسم شروع به جوشیدن می كند.
اسلاید 3 :
- جرم يك حجم واحد از يك جسم را چگالي مينامند.
- ارشميدس كشف كرد كه اگر جسمي را در آب فرو برند، مقداري از وزن آن كاسته ميشود.
- مقدار كاهش وزن مساوي با وزن آبي است كه جسم جاي آن را گرفته است.
- اين دانشمند تاجي را در آب فرو برد و آب جابجا شده را اندازه گرفت.
- بعد قطعهاي طلا كه وزنش مساوي تاج بود در آب فرو برد و آب جابجا شده را اندازه گرفت.
- آنگاه ديد كه تاج بيشتر از طلا آب را جابجا كرده است و فهميد كه تاج از طلاي خالص نيست.
- اما اگر يك قطعه نقره و يك قطعه طلا با حجم مساوي را درنظر بگيريم، ميتوانيم بگوييم طلا سنگينتر است.
- جرمهايي كه حجم مساوي داشته باشند و از اجسام مختلف باشند، چگالي مختلف دارند.
- چون تاج از قطعه طلايي كه حجمش با آن مساوي بود، سبكتر بود لذا چگالي آن كمتر بود.
- واحد چگالي در سيستم متريك، گرم بر سانتيمتر مكعب است.
اسلاید 4 :
- براي اينكه چگاليها را بصورت عدد درآوريم، بايد اجسامي را كه چگالي مختلف دارند با يكديگر مقايسه و مقياس اصلي را انتخاب كنيم.
- دانشمندان براي مايعات و جامدات، آب و براي گازها، هوا را مقياس اصلي قرار دادهاند.
- يك سانتيمتر مكعب آب، يك گرم جرم دارد.
- بنابراين چگالي آب در سيستم متريك، يك گرم بر سانتيمتر است.
- نسبت چگاليها به مقياس اصلي را با كلمهي (( مخصوص )) نشان ميدهيم.
- نسبت چگالي يك جسم به چگالي مقياس اصلي، وزن مخصوص ناميده ميشود.
- مثلاً چگالي طلا 3/19 گرم در سانتيمترمكعب است، يعني يك سانتيمتر مكعب طلا جرمي معادل 3/19 گرم دارد.
- بنابراين طلا 3/19 برابر آب چگالي دارد يا وزن مخصوص طلا 3/19 است.
- ما ميتوانيم چگالي هر يك از حالتهاي ماده يعني جامد و مايع و گاز را تعيين كنيم.
- ابتدا جرم آن و سپس حجم آن را معين ميكنيم، آنگاه جرم را به حجم تقسيم ميكنيم تا چگالي را بدست آوريم. جرم را ميتوانيم با ترازو معين كنيم.
- ما ميتوانيم حجم جامداتي را كه شكل منظم دارند محاسبه كنيم.
- براي تعيين حجم جامداتي كه شكل منظم ندارند، آنها را در آب فرو ميبريم و حجم آب جابجا شده را اندازه ميگيريم.
اسلاید 5 :
- A physical change takes place without any changes in molecular composition.
- The same element or compound is present before and after the change.
- The same molecule is present through out the changes.
- Physical changes are related to physical properties since some measurements require that changes be made.
- Melting Point:
- As solid matter is heated it eventually melts or changes into a liquid state at the melting point.
Ice (a solid form of water) melts at 0 oC and changes to the liquid state. - Carbon dioxide melts at -56.6oC
- Boiling Point:
- As the liquid matter is heated further it eventually boils or vaporizes into a gas at the boiling point.
Liquid water boils and changes into a gas, usually called steam or water vapor at 100 oC. In all three states the same molecules of water (H2O) are present.
اسلاید 6 :
- Reactivity
- Heat of combustion
- Enthalpy of formation
- Toxicity
- Chemical stability in a given environment
- Flammability
- Preferred oxidation state(s)
- Coordination number
- Capability to undergo a certain set of transformations, for example molecular dissociation, chemical combination, redox reactions under certain physical conditions in the presence of another chemical substance
- Preferred types of chemical bonds to form, for example metallic, ionic, covalent
- For example, hydrogen has the potential to ignite and explode given the right conditions. This is a chemical property.
- Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas. This is a chemical property.
اسلاید 7 :
- Chemical Properties:
- Chemical properties of matter describes its "potential" to undergo some chemical change or reaction by virtue of its composition.
- What elements, electrons, and bonding are present to give the potential for chemical change.
- It is quite difficult to define a chemical property without using the word "change". Eventually you should be able to look at the formula of a compound and state some chemical property.
- At this time this is very difficult to do and you are not expected to be able to do it.
- For example hydrogen has the potential to ignite and explode given the right conditions. This is a chemical property.
- Metals in general have they chemical property of reacting with an acid.
- Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas. This is a chemical property.
اسلاید 8 :
- Chemical Changes or Reactions:
- Chemical change results in one or more substances of entirely different composition from the original substances. The elements and/or compounds at the start of the reaction are rearranged into new product compounds or elements.
- A CHEMICAL CHANGE
- alters the composition of the original matter. Different elements or compounds are present at the end of the chemical change.
- The atoms in compounds are rearranged to make new and different compounds.
- Magnesium reacts with oxygen from the air producing an extremely bright flame.
- This is a chemical change since magnesium oxide has completely different properties than magnesium metal shown on the left.
- Safety: Do not try this without supervision and DO NOT LOOK DIRECTLY AT THE LIGHT!
- The atoms are rearranged - diatomic oxygen molecules are split apart so that one oxygen atom combines with one magnesium atom.
اسلاید 9 :
- Oxidation of Iron - a chemical change:
- For example iron has the potential to rust given the right conditions. This is a chemical property.
- If iron does rust, this is a slow chemical change since rust is an iron oxide with different properties than iron metal.
- In the graphic on the left, iron or steel wool is burning in a fast reaction with oxygen as contrasted with the slow rusting of iron also with oxygen.
- In the element iron only atoms of iron are in contact with each other. In the element oxygen each oxygen is joined with one other to make a diatomic molecule. These atoms and molecules are rearranged so that two iron atoms combine with three atoms of oxygen to form a new compound.
اسلاید 10 :
- The standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states (the most stable form of the element at 1 bar of pressure and the specified temperature, usually 298.15 K or 25 degrees Celsius). Its symbol is ΔHfO or ΔfHO.
- For example, the standard enthalpy of formation of carbon dioxide would be the enthalpy of the following reaction under the conditions above:
- C(s,graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) The standard enthalpy of formation is measured in units of energy per amount of substance. Most are defined in kilojoules per mole (kJ mol−1), but can also be measured in calories per mole, joules per mole or kilocalories per gram (any combination of these units conforming to the energy per mass or amount guideline). In physics the energy per particle is often expressed in electronvolts which corresponds to about 100 kJ mol−1.
- All elements in their standard states (oxygen gas, solid carbon in the form of graphite, etc.) have a standard enthalpy of formation of zero, as there is no change involved in their formation.